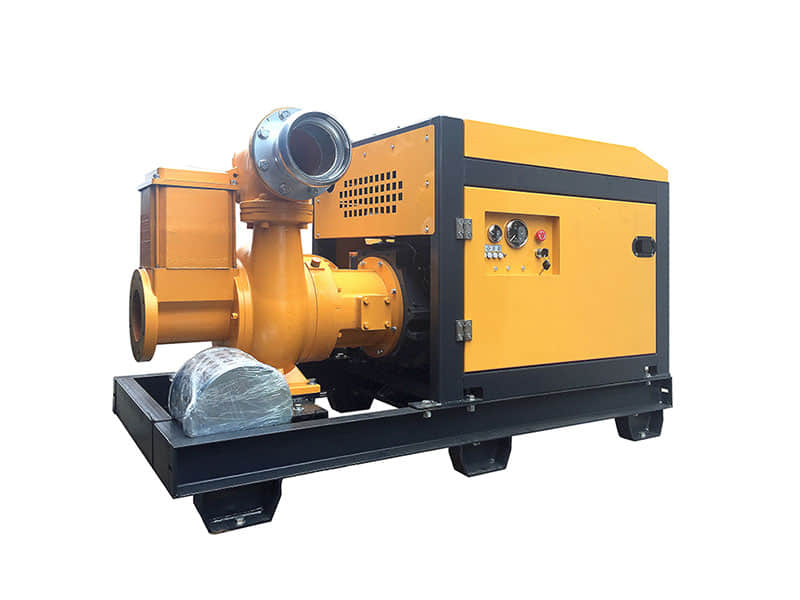
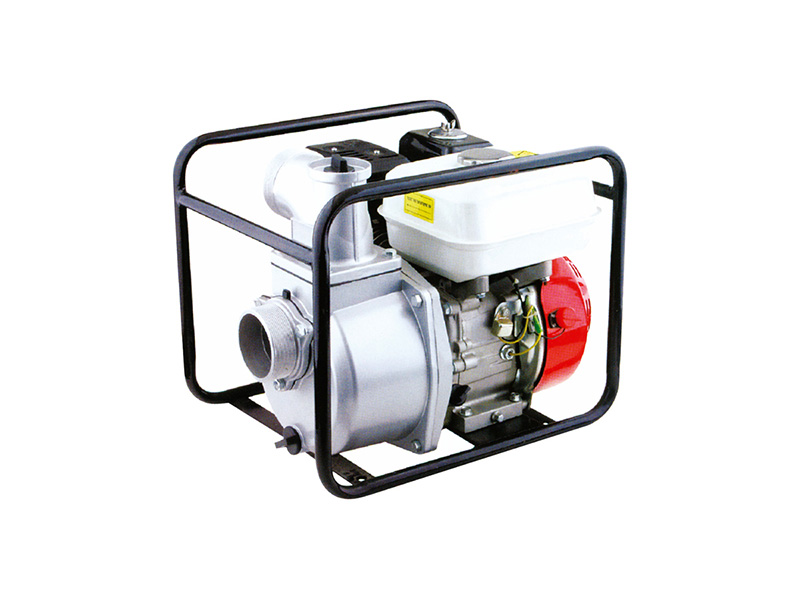
HWP50G/80G/100G Portable Water Pump
Inlet/Outlet Size
HWP-50: 2''(50mm)
HWP-80: 3''(80mm)
HWP-100: 4''(80mm)
Displacement Q.Max(M³/5)
HWP-50: 30
HWP-80: 45
HWP-100: 80
Max.Output(HP)
HWP-50: 5.5
HWP-80: 5.5
HWP-100: 6.5
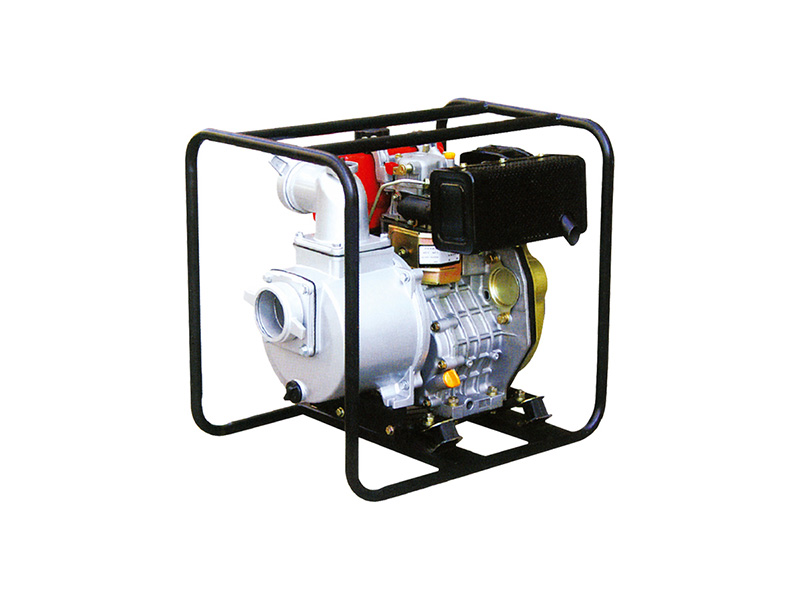
HWP50D/80D/100D Portable Water Pump
Inlet/Outlet Size
HWP-50: 2''(50mm)
HWP-80: 3''(80mm)
HWP-100: 4''(80mm)
Displacement Q.Max(M³/5)
HWP-50: 30
HWP-80: 45
HWP-100: 80
Max.Output(HP)
HWP-50: 5.5
HWP-80: 5.5
HWP-100: 6.5
What Are Water Pumps?
Water pumps, in their mechanical or electromechanical essence, are designed for the propulsion of water through pipes or hoses by establishing a pressure differential. Among the plethora of pumps for water movement, centrifugal pumps and positive displacement pumps are predominantly utilized. The centrifugal variety harnesses centrifugal force to channel water into an impeller, converting rotational energy into hydrodynamic energy.
Diverse Water Pump Categories
The spectrum of water pumps is vast, catering to distinct needs. Positive displacement pumps, for example, utilize mechanisms like a piston, diaphragm, or cog to consistently transport a defined fluid volume. These pumps maintain a constant flow rate, independent of inlet pressure, a feat not achievable by centrifugal pumps.
Applications of Various Water Pumps
- Automotive Water Pumps: Employed in vehicle engines for circulating coolant, these impeller pumps are integral in preventing engine overheating and in cooling fluid circulation.
- Agricultural Water Pumps: Essential in farming, these pumps facilitate irrigation, ensuring crop hydration, often involving water treatment or fertilizer addition before application.
- Boiler Water Circulating Pumps: In the heating sector, these pumps distribute heated water through a pipe network, transferring thermal energy to radiators or convectors for room heating.
- Dewatering Pumps: Crucial in construction, these pumps extricate ground or surface water, enabling excavation and foundational work.
- Groundwater Remediation and Sampling Pumps: Used at polluted sites for water extraction and treatment, or for water quality sampling and testing.
- Industrial Water Pumps: A broad category encompassing heavy-duty pumps used in various industries like manufacturing, oil & gas, and more.
- Saltwater or Sea Water Pumps: Specifically designed to resist the corrosive nature of saltwater, these pumps are common in marine applications.
- Stormwater Pumps: Used for transferring stormwater from collection points to treatment or sewer systems, often employing electrically operated submersible pumps.
- Sump Pumps: Integral to waterproofing systems, these pumps prevent flooding by discharging water accumulating in building low points, like basements.
- Wastewater Pumps: Transport wastewater to treatment facilities, often incorporating inlet strainers to handle soil and sediment.
- Waterworks and Water Treatment Pumps: Critical in water supply systems, these pumps are used for water pressure maintenance and in treatment processes.
Gas Water Pumps
In addition to the above categories, gas water pumps warrant a mention. These pumps, powered by gasoline, are often preferred for their portability and high power output, making them ideal for applications where electric power is unavailable or insufficient.
How To Select a Water Pump
Confronted with a myriad of water pump choices? Pondering over petrol versus diesel, electric or engine-driven, firefighting or trash pumps?
Part 1 – Types of Pumps
- Engine-Driven Pumps: These combustion engine-driven pumps, available in petrol or diesel, boast portability and independence from electricity. Horizont specializes in this category, offering diverse designs and sizes.
- Electric-Powered Pumps: Ranging in sizes and designs, these are typically stationary, suited for continuous operations like supplying water to buildings. Portable variants exist but require electrical access.
- Jet Pumps: Ideal for extracting water from deep sources like bores or wells, jet pumps come in both electric and engine-driven models.
- Diaphragm Pumps: Unlike centrifugal pumps, these handle thick fluids like sewage or mud-laden water.
- Stationary Pumps: Large-scale, often used in industrial or agricultural settings, available in electric or diesel-powered versions.
Part 2 – Pump Applications
- Firefighting: Essential for home fire protection, especially where mains electricity might be unavailable. Independent power sources like generators or engine-driven pumps are crucial.
- Water Transfer: Suitable for relocating water from various sources. Key factors include performance requirements and portability.
- Dirty or Debris-Filled Water: Trash pumps are designed to safely handle water with solids, ideal for dewatering sites or floodwater management.
- Effluent or Chemical Movement: Chemical-resistant pumps, made from corrosion-resistant materials, are necessary for handling harmful substances.
- Supplying Water to Buildings and Gardens: Electric pumps, often with a jet mechanism, are commonly used for prolonged and on-demand operations.
Part 3 – Pump Attributes
Performance Metrics:
- Flow Rate: Measured in liters per minute, crucial for assessing the volume of water moved.
- Max Head: The vertical distance a pump can elevate water, crucial for calculating suction and uplift requirements.
- Pressure: Measured in PSI, important for determining how far and efficiently a pump can transport water.
Reliability and Quality: Choose trusted brands with quality materials. Horizont, for instance, uses premium engines and durable materials like cast aluminum and stainless steel.
Warranty: Opt for brands offering warranties for assurance and support.
Service and Support: Prefer brands with accessible service networks. Horizont, being Australian-operated, offers local support.
Fuel Type: Choose between petrol and diesel based on cost, efficiency, and safety considerations.
Water Master Pump Options
- Firefighting Pumps: High
- pressure, moderate flow, versatile for both fire defense and water transfer.
- Transfer Pumps: High flow, moderate pressure, ideal for moving clean water in various sizes.
- Trash Pumps: High flow, moderate pressure, designed for water containing solids and debris.
For further inquiries or assistance, contact us at +86 16762215115. This comprehensive guide is tailored to help you navigate the complexities of choosing the suitable water pump, incorporating "Gas Water Pumps" as a vital aspect of the selection process. Whether for domestic, agricultural, or industrial purposes, understanding pump types, applications, and key attributes will lead you to the right choice.
How to Select a Gasoline Water Pump
Navigating the choice of the perfect gasoline water pump for various needs like irrigation, construction, drainage, or emergency water supply involves several key considerations. Bonhoeffer Machines presents a range of high-quality gasoline water pumps, and here's how to pick the most suitable one:
Pump Varieties:
Gasoline water pumps come in different forms, including centrifugal and diaphragm pumps. Centrifugal pumps excel in general water transfer and irrigation tasks, while diaphragm pumps are adept at handling water with mud or sand and can manage solid materials effectively.
Flow and Lift Capacities:
Assess the required flow rate (in gallons per minute, GPM) and head (the height to which the pump can elevate water, measured in feet). Your choice should align with the distance and elevation required for your specific water pumping task.
Engine Strength:
These pumps are engine-driven, typically gauged by horsepower (HP). Selecting an engine with the appropriate horsepower is crucial; higher HP facilitates greater flow rates and voluminous water handling.
Transportability:
If mobility is key, opt for a gasoline water pump that's easy to relocate. Compact designs, lightweight structures, and features like built-in handles or wheels enhance portability.
Durability and Build Quality:
Choose pumps constructed for tough environments. Pumps made from robust materials like cast iron or aluminium, equipped with high-quality seals and gaskets, offer extended durability and consistent performance.
User-Friendly and Maintenance Aspects:
Ease of operation is important. Features such as simple start-up, fuel efficiency, and accessible controls add to the user-friendliness. Maintenance simplicity, with available parts and straightforward servicing schedules, is also vital.
Safety Considerations:
Look for safety elements like low oil shutdown, spark arrestors, and solid frames for protection and accident prevention.
Customer Feedback and Brand Reputation:
Investigate customer experiences and reviews of various gasoline water pump models and brands. Brands with a strong reputation for quality and excellent customer service are often more reliable.
By carefully evaluating these aspects and aligning them with your specific needs, you can make an informed decision on the gasoline water pump that will effectively fulfill your water pumping requirements.